Nutrition and Metabolism PhD Program
Nutrition researchers are a critical part of our society as they examine the complex interplay between nutrients, health, and disease, spanning from the individual to populations. With careers as faculty or independent scientists in academia, industry, and government, graduates of the Nutrition and Metabolism (N&M) PhD Program are at the forefront of research. They are making important contributions linking diet to the maintenance of health and impact on disease prevalence, and educating the public on the critical role of diet in the maintenance of optimal health throughout the life cycle.
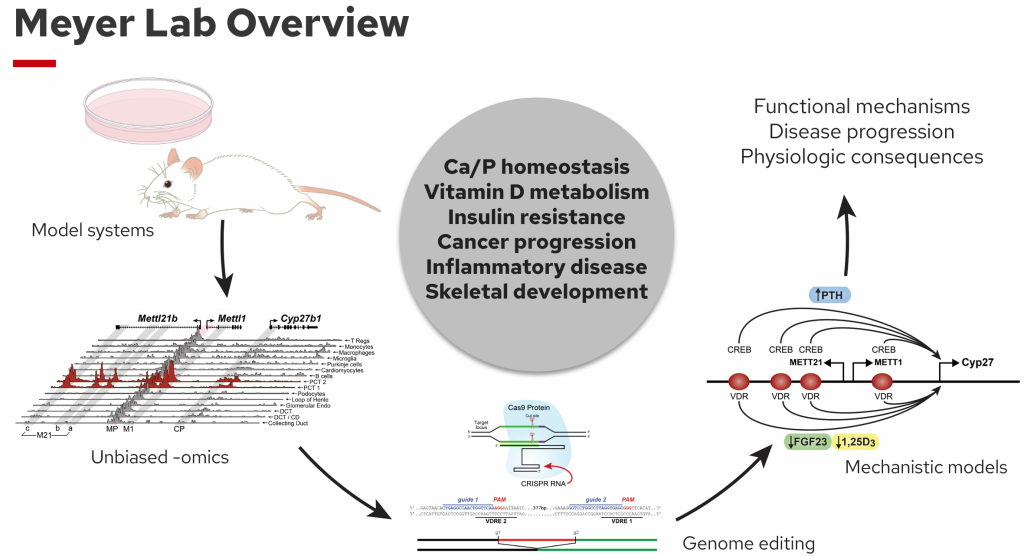
Research
52 faculty trainers across 17 departments provide extensive interdisciplinary training opportunities in molecular, human and animal nutrition research.

Program Requirements
Our flexible curriculum provides core nutrition and metabolism coursework, with ample opportunities for elective coursework and minors.

Student Life
Gain a world-class education in a world-class city. Madison is a vibrant and inclusive community, and is consistently ranked as one of the best places to live in the U.S. for quality of life.
“Whether you’re driven by discovery, problem-solving, or the pursuit of knowledge, we look forward to helping you shape your research journey and make meaningful contributions to your field.“
-Dr. Rick Eisenstein, Director of Graduate Studies
News & Events
-
Jake Hermanson awarded F31 Fellowship
Nutrition and Metabolism Ph.D. candidate Jake Hermanson of the Leone Lab has been awarded a three-year F31 Fellowship from the National Institutes of Health for his project, “The role of dietary cholesterol in Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through the action of gut microbiota.” Congratulations, Jake!
Recent Publications
Armstrong MT, Antunes K, Willis NB, Meyer MB, Pierre JF, Ozturk G. Whey Protein Phospholipid Concentrate and Its Fractions as a Diet Intervention Enhance Bone Health and Alter the Gut Microbiome in Weanling Mice. FASEB J. 2025 Dec 15;39(23):e71260. doi: 10.1096/fj.202502683R. PMID: 41363910; PMCID: PMC12687760.
Hermanson JB, Tolba SA, Gazi MA, Chrisler EA, Kaur M, Sidebottom AM, Liu Y, Martinez-Boggio G, Lucas LN, Amador-Noguez D, Rey FE, Leone VA. Gut microbes mediate the synergistic effects of dietary cholesterol and saturated fat in driving fibrosing MASH. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 21:2025.07.16.665145. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.16.665145. PMID: 40777228; PMCID: PMC12330582.
Elliehausen CJ, Olszewski SS, Minton DM, Shult CG, Ailiani AR, Trautman ME, Babygirija R, Lamming DW, Hornberger TA, Konopka AR. Rapamycin Does Not Compromise Exercise-Induced Muscular Adaptations in Female Mice. Aging Cell. 2025 Jul 24:e70183. doi: 10.1111/acel.70183. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40704394.
Bui H, Hansen JK, Lo Sardo V, Galmozzi A. White and Brown Adipose Tissue Share a Common Fibro-Adipogenic Progenitor Population. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 30:2025.05.28.656577. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.28.656577. PMID: 40501707; PMCID: PMC12154837.
Lee SM, Cichanski SR, Pintozzi NG, Kaufmann M, Jones G, Meyer MB. Kidney deletions of Cyp27b1 fail to reduce serum 1,25(OH)2D3. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2025 Jun;250:106734. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2025.106734. Epub 2025 Mar 15. PMID: 40096920.
Willis NB, Mims T, Antunes K, Peng H, Yen CE, Pierre JF. Intermittent Parenteral Nutrition Reduces Peroxisomal Lipid Oxidation Pathway Transcripts Compared to Continuous Isocaloric Infusion. Physiology. 2025;40(S1):1225. doi:10.1152/physiol.2025.40.S1.1225
McGregor ER, Lasky DJ, Rippentrop OJ, Clark JP, Wright S, Jones MV, Anderson RM. Reversal of neuronal tau pathology via adiponectin receptor activation. Commun Biol. 2025 Jan 4;8(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07391-z. PMID: 39755746; PMCID: PMC11700159.
Antunes K, Leathem C, Mims T, Willis N, Pierre J. (2024). Colostrum Supplementation to Rescue Antibiotic-Induced Dysbiosis and Reduce Long-Term Obesity Risk. Physiology, 39(Suppl 1), Abstract 2180.
Hermanson JB, Tolba SA, Chrisler EA, Leone VA. Gut microbes, diet, and genetics as drivers of metabolic liver disease: a narrative review outlining implications for precision medicine. J Nutr Biochem. 2024 Nov;133:109704. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109704. Epub 2024 Jul 17. PMID: 39029595; PMCID: PMC11480923.
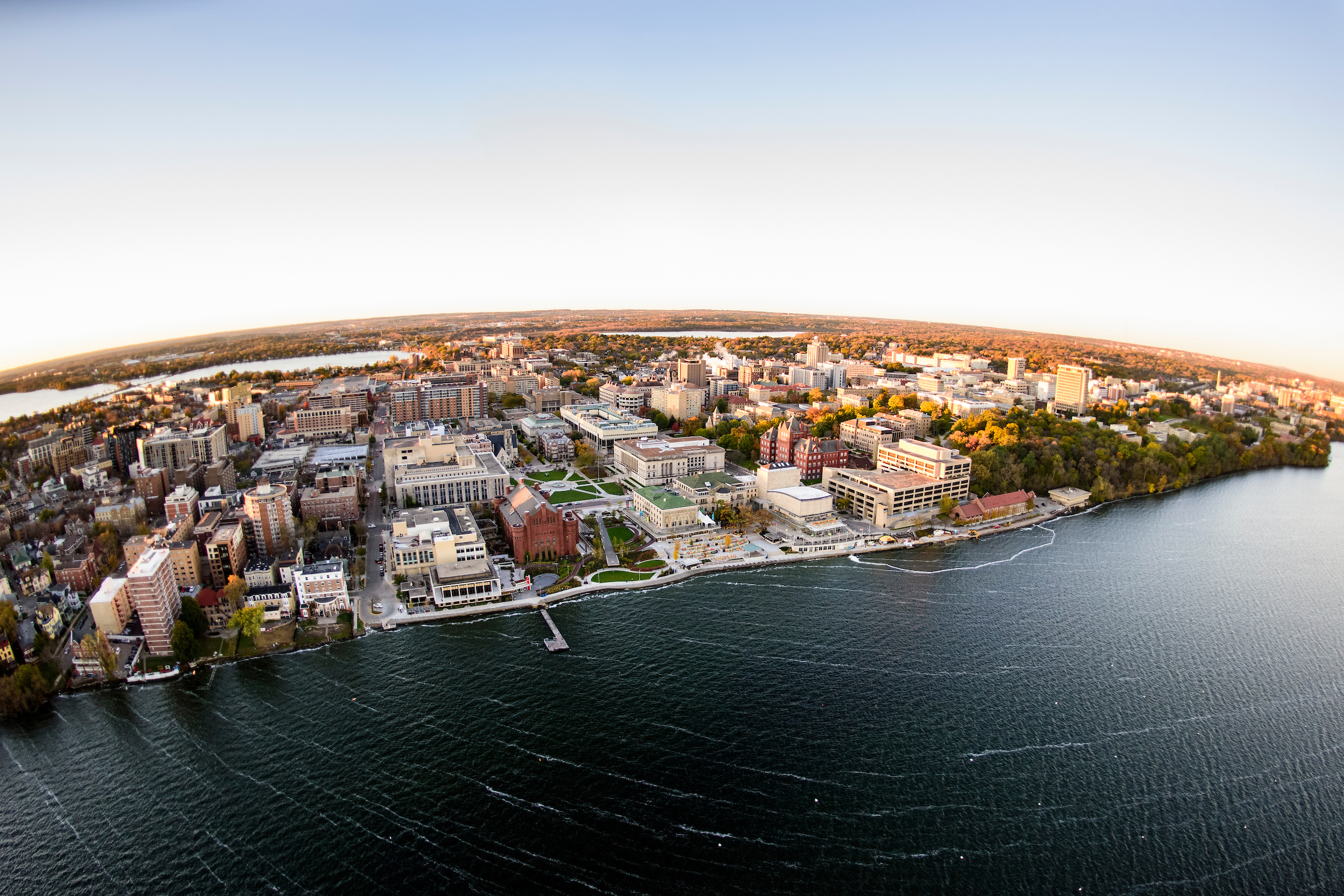
The University of Wisconsin–Madison rests in the ancestral land of the Ho-Chunk Nation, the People of the Big Voice, who have called this place Teejop (day-JOPE) for time immemorial. We as a university community continue to create and build upon our partnerships with the 12 First Nations of Wisconsin. As a state university we respect the inherent sovereignty and unique legal status, as affirmed and set forth in state and federal law, of the First Nations of Wisconsin.